Mono Sodium Phosphate / Monobasic Sodium Phosphate / Sodium Phosphate Monobasic / Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate / Sodium Dihydrogen Orthophosphate Manufacture in India.
Monosodium phosphate (MSP), also known as anhydrous monobasic sodium phosphate and sodium dihydrogen phosphate, is an inorganic compound of sodium with dihydrogen phosphate (H2PO4−) anion. One of many sodium phosphates, it is a common industrial chemical. It exists as an anhydrous salt, as well as mono- and dihydrates.
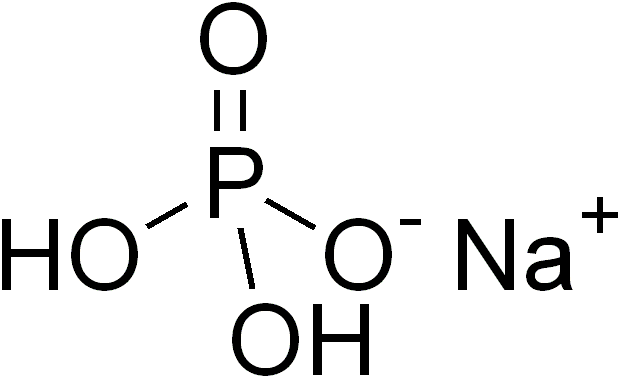
- Cas No:
- 7558-80-7
- Formula:
- NaH2PO4
- Molecular Weight:
- 120.0
- Character:
- White Slightly deliquescent crystals Or granules, very soluble in water, very slightly soluble in ethanol 96%
- Packaging:
- 25/50 Kg. HDPE bags with polyliner inside.
- Storage:
Available Grade & Specification
| Item | FCC | BP | USNF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assay | NLT 98.0% & NMT 100.5% of NaH2PO4 on dried material | NLT 98.0% & NMT 103.0% if NaH2PO4 on anhydrous basis | NLT 98.0% & NMT 103.0% if NaH2PO4 on anhydrous basis |
| Identification | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Acidity(pH) | 4.2 to 4.5 | 4.1 to 4.5 | 4.1 to 4.7 |
| Clarity & color of solution | Pass the test | ||
| Arsenic | 2 ppm Max | 8PPM Max | 3PPM Max |
| Heavy Metals | 10 PPM Max | 0.002% Max | 4PPM Max (as Pb) |
| Iron | 10 PPM Max | ||
| Chloride | 200 PPM Max | 0.014%% Max | 10 PPM Max |
| Sulphates | 300 PPM Max | 0.15 % Max | |
| Reducing substances | Pass the test | ||
| Loss on drying | 1.0% Max | LT 2.0% | 2.0% Max |
| Insoluble substances | 0.2% Max | 0.2% Max | |
| Aluminium calcium & related elements | Pass the test | ||
| Organic volatile impurities | Pass the test | ||
| Fluoride | 0.005% Max |
Application & Industries
In baking powder,
As dry Acidulant for foods,
As sequestrant for foods.
Cattle food supplement,
Buffer,Emulsifier, Nutrient supplement.
Monosodium phosphate (MSP) or Anhydrous monosodium phosphate is a common pharmaceutical chemical Monosodium phosphate (MSP) or Anhydrous monosodium phosphate is a common pharmaceutical chemical having a white crystal-like appearance. One of many sodium phosphates, MSP is an inorganic sodium compound with a dihydrogen phosphate anion (H_2 PO_4^-). It has an IUPAC name of Sodium dihydrogen phosphate and is also known under the name, Monobasic sodium phosphate, Sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate, and Sodium phosphate monobasic. Generally, the salt exists in three forms: anhydrous, monohydrate and dihydrate. Therefore also knows as Monobasic sodium phosphate Anhydrous, Sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate Anhydrous, and Sodium phosphate monobasic Anhydrous. Monobasic sodium phosphate Monohydrate , Sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate Monohydrate , Sodium phosphate monobasic Monohydrate. Monobasic sodium phosphate Dihydrate , Sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate Dihydrate, and Sodium phosphate monobasic dihydrate.
What does Hydrate Stand for ?
Hydrate is any compound that contains water of crystallization and when a hydrate contains one mole of water per mole of compound, we obtain a monohydrate.
The Anhydrous form of this compound is useful in various ways:
1. It is used as a food additive in animal feed, evaporated milk, and toothpaste.
2. It is used as an emulsifier as well as a thickening agent.
3. The presence of magnesium ion can be detected with the help of this salt.
The monohydrate form of monosodium phosphate is a reagent with a large buffering capacity. This inorganic sodium compound finds wide application in the field of biochemistry, molecular biology, and chromatography.
It has various alternative names such as: Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate; Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate; Sodium dihydrogen phosphate hydrate and Phosphoric acid, monosodium salt, monohydrate.
The monohydrate salt is used in the:
1. Purification of antibodies.
2. Manufacture of leather and textile products.
Dihydrate form of monosodium phosphate.
As a matter of fact, we obtain a dihydrate when two moles of water combine with per mole of compound. A highly hygroscopic and water-soluble compound, monosodium phosphate dihydrate is a reagent with a large buffering capacity.
It has various alternative names such as: Sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate; Sodium phosphate monobasic dihydrate; and Phosphoric acid, monosodium salt, dihydrate.
The dihydrate salt is used:
1. As a flavoring reagent and a food additive.
2. In the manufacture of paper and pulp products.
